CLIVAL HEMANGIOMA


CLIVAL HEMANGIOMA MRI & CT Findings with Differential Diagnosis
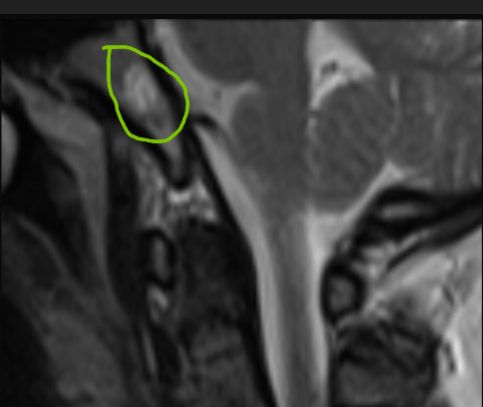
*Case Summary: 8 mm nodular lesion in the clivus, hyperintense on T1 and T2.
*What is a Clival Hemangioma?
•Benign vascular tumor arising within bone
•Usually incidental finding
•Often asymptomatic
*Why Hyperintense on T1?
•High signal from vascular pools and fatty content
•T1 hyperintensity is a typical feature
*Why Hyperintense on T2?
•High water content and vascular channels → long T2 signal
•Bright, well-defined appearance on MRI
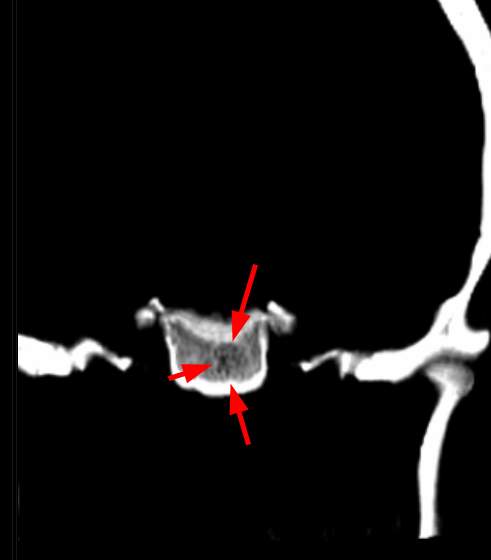
*Clue: Typical trabecular (“polka-dot”) pattern on CT
💡 Why Polka-Dot Pattern on CT?
Bone trabeculae preserved between vascular channels
Small round densities on axial CT
Key differential diagnostic feature
*Clival Hemangioma – Differential Diagnosis
•Chordoma: Midline, destructive, very hyperintense on T2 with septations (“soap-bubble”).
•Chondrosarcoma: Off-midline, chondroid calcification (“rings & arcs” pattern).
•Meningioma: Dural-based, homogeneous strong enhancement, often with “dural tail”.
•Metastasis: Variable, usually heterogeneous, marked bone destruction with soft-tissue mass.
•Plasmacytoma: Solitary, lytic, sharply demarcated, homogeneous enhancement.
•Hemangioma: Hyperintense on T1/T2, honeycomb or polka-dot trabecular pattern, expansile but less aggressive.
*Contrast was not used in this case. If administered, hemangioma usually shows early homogeneous enhancement, followed by contrast gradually filling the internal spaces. This creates:
•“Puzzle-piece” pattern: Different compartments of the lesion enhance at different times,
resembling puzzle pieces fitting together.
•“Filling-in” pattern: Over time, contrast fills the lesion completely, becoming uniformly enhanced.